How page load speed affects SEO
Before we start to elaborate on how page speed can affect SEO. Let’s start by answering the first question that’s on your mind:
What is page speed?
Page speed is the time that a specific page takes to display its content completely, also known as “page load time.” It can be defined similarly as “time to first byte” or “TTFB.” In essence, it is the time when the browser collects the first byte of information from a web server. Sometimes, page speed is often mistaken for “site speed,” which is normally the speed of page views on a website.
What is the importance of Page Speed in SEO
Page load speed is a very important aspect to consider when we do SEO. In fact, Google has made page speed a ranking factor. Which means that is has a direct impact on rankings. Hence, Google has provided developers and webmaster with a set of tools in order to improve websites loading speed, such as:
- Google Light House
- PageSpeed Insight
How is page load speed evaluated
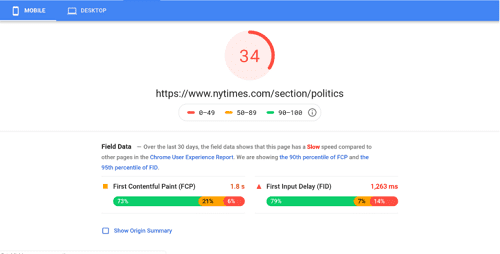
Generally, you can find tools that are available on the Internet to help evaluate the loading time of a page. The most common one is PageSpeed Insights and Google Lighthouse. Most SEO copywriters prefer to use PageSpeed Insights. Because it always delivers accurate data, including CrUX (Chrome User Experience Report). It also gives the user two significant speed metrics:
- First Contentful Paint (FCP)
- DOMContentLoaded (DCL)
How a page is loaded on a website
- A user makes a request by clicking on a link
- The page requested is then downloaded along with all its resources/files
- To create the page, the web browser will then make use of the page resources
- Thereafter, the page will be displayed to the user
As most users know, a page takes a few seconds before an entire page fully loads. Consequently, after the first 1.5 seconds, the user that lands on your page gets the “First Meaningful Paint.” Which is the content displayed above the fold. When you land on a page and stare at a white screen whilst the page is loading for a couple of seconds, this is TTFB at work. The First Meaningful Paint or First Contextual Paint is the time taken for a page to load enough data allowing the user to start reading the content on your page. Remember, your page is fast the sooner a player can start interacting on your page.
How to improve your page speed
Are you not very happy about the score obtained from PageSpeed Insight?
Hold on, you can remedy to that…
Here are four ways to obtain a perfect PageSpeed Score:
1. Compress your Images
The main cause affecting the page speed is large images presented on a page. To fix this issue, the go-to technique is to compress them. You can easily find websites that can bring down to 50% compression of large images for free. Please see below the most common ones:
2. Minify HTML
Reducing the space occupied by your HTML coding is another important factor in getting a perfect Google score. Minification is the process of deleting or correcting unnecessary or duplicated data without impacting the way a browser processes HTML code.
This involves correcting the code, formatting, deleting the unused code, and shortening the code when possible. Thanks to the great WordPress plugin options available, you longer need to be a coding genius to solve this problem.
3. Browser caching
Browser caching is another tool that can have a big impact with relatively little effort when it comes to page speed. Getting the resources to load your website takes tons of effort. This requires loading each image and page element and then managing the HTML and coding. Each time a user loads your site, this process is continuously repeating itself. Which causes your site to take a long time to load. Browser caching can definitely help with this issue. Basically, it memorizes resources previously loaded so that you don’t have to recharge them at each time. All of your page data such as logos and footers don’t need to be reloaded each time a visitor visits a new page on your site. By caching your browser, your page speed will when people land on your site.
4. AMP Implementation
AMP is the abbreviation for Accelerated Mobile Pages. This is a project implemented by Google to speed up the loading of mobile pages. It works by creating an open-source format that removes tons of unnecessary content, allowing your mobile pages to load almost instantly. It offers users a more streamlined experience on mobile without any awkward functionality that doesn’t work well on mobile devices. If you are browsing the Internet on your mobile phone, you have probably clicked on an AMP-based article.


