Details on the July 2021 Core Update
After the much-anticipated June 2021 Core Update Google announced a two-part update on their search liaison Twitter account. The Google July 2021 Core Update rolled out on July 1, and it was said to typically take one to two weeks to finish.
The June update took ten days to roll out; however, most updates take a full 14 days to roll out. Google pre-announcing the July 2021 core update was an unusual step. However, the update still created a shock wave amongst the SEO industry. The broad core algorithm update lasted 14 days, concluding on July 12.
The June 2021 core update change was visible across 31 categories, and Google did warn that some sites would see a reversal between the June and July updates. With that, the data and outcomes of these updates were further mudded by the fact that Google’s page experience update, which focused on Core Web Vitals, also launched in June.
So, what can be taken from the July update, and how were websites affected. We get into the nitty-gritty analysis of the July core update right here.

July 2021 Core Update Analysis
We have come to learn that each core update is a significant event that webmasters should carefully monitor. Likewise, the July 2021 core update was a unique one. When announcing the June 2021 Update, Danny Sullivan from the Google Search Liaison indicated that a second broad core update in July would follow the June update.
The reasoning for the second core update was that there were aspects of the June update that were not fully ready. Rather than waiting for all elements of the update to be ready for the rollout, Google decided to release the core update in two separate parts, June 2021 and July 2021 core update. So, what is the connection between these two updates, and what exactly happened in the July 2021 update.
The two most comparable aspects between the June and July update are the rank stability as well as mobile data. SEMrush made a comparison between the volatility increases from June and July to see which update had more impact overall.
1. Rank Stability
They made this comparison by tracking the period of rank stability in both months. The results showed a 42% rank volatility increase in June which was more significant than what they spotted in July. This was the case across several Industries such as travel, house, news, food & drink, books & leisure as well as arts & entertainment and many others.
2. Mobile Data
In terms of mobile data, when compared to desktop rank stability, mobile showed a larger gap between the June and July updates. The desktop volatility increased with an average of 42% on the desktop, while on mobile, it was 47%.
With the comparison did by SEMrush, we could see that the industries with the highest inconsistencies between the June and July core update are:
- Law & government, as well as the jobs & education sectors which were 70% more volatile during the June update.
- Health & travel sectors were 65% more significant after the June update.
- Lastly, the game sector was 54% more volatile after the June update.
Is The July 2021 Core Update A Reversal Of The June Update?
We have noticed that a web page can be negatively impacted by an update only to be restored at the end of the rollout. So, many webmasters brought up the question of whether the July update was a reversal of the June update due to the purposeful connection between the two. When looking at the top 200 domains that were impacted by the update, only 15 were impacted during both updates.
From those 15, only 10 show their ranking reverse between the June and July updates. This is basically 5% of the total 200 websites showing a reversal. This indicates that the July update was fundamentally not a reversal of the June update. Rather it shows that each of the core updates impacted websites uniquely.
So, What Should SEOs And Webmasters Do
In 2019 Google published a post on its Google Search Central Blog explaining the algorithm technicalities behind core updates and what you as a webmaster can do if you are affected by a core update, whether you have been hit negatively or positively by the update.
It does not mean you have violated Google’s guidelines. You simply have to remember that the changes are based on Google’s assessment of content overall.
Google also recommends that if your website has been affected by an update, you should focus on offering the best content that you can. They also listed a set of questions that you can ask yourself about your content if you have been hit by an update.
- Content And Quality – is the content on your website original, does it offer valuable information, are your headlines and titles descriptive, is there a helpful summary of the content? Also, would you share that content with your friends or family?
- Expertise – are there any errors on your site? Is your content trustworthy, also? If you, as the webmaster, had to come across your site on Google, would you trust it?
- Presentation and Production – the content on your website has to be well produced and researched. How many ads appear on your content also how does your content display on different devices.
- Comparative Questions – does your website have added value compared to what your competitors have? Also, will your content meet the expectations of your users?

Bring in E.A.T
With that, it’s also important to remember that with Google, correlation is not causation. What this means is that even if your website passes the Core Web vitals matrix, receives backlinks, features top keywords in its page titles, it does not mean that these factors necessarily cause changes in your rankings.
There were many other accrediting factors that could potentially serve as ranking factors when Google’s algorithm. Google’s core updates serve as an indication that it is becoming more sophisticated in understanding user experience and intent. So, it is possible that the content that you had in 2019 was more user-friendly than what you have in 2021, which is why you could be negatively hit by a core update and vice versa.
Also, in checking whether your content is now in correlation with the latest score update, there are a few elements that you could use to check your content. For instance, you can improve E.A.T, which is the expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness of your content.
- Check which keywords have had the biggest loss in ranking position;
- Check which pages have seen the biggest drop in clicks;
- Also, do a complete competitor analysis.
Is the July update mobile-based?
While there is no direct indication that the July core update was mobile-focused however the June core update was mobile-first, then desktop. The June core update looked at
- How long website take to load;
- What the user experience is like;
- How secure your website and your visitor’s data is;
- as well as how accessible websites are on mobile.
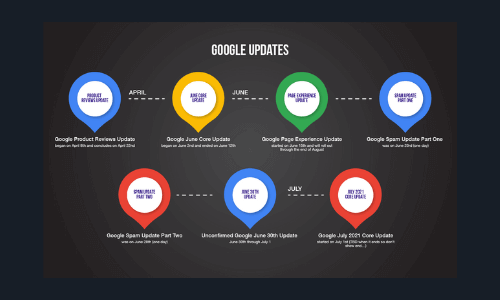
What Else Is Happening On Google
In the past few months, Google has had a few search update rollouts. Here is a list of all the updates that have hit our sites so far
- 8-22 April – The Product Reviews Update
- 2- 12 June – June Core Update
- 15 June until end of August – Page Experience Update
- 23 June – Spam Update Part 1
- 23 June – Spam Update Part 2
- 1 to July 26 – July Core Update
So, as we speak, the page experience update is still ongoing, as well as the spam update part 2. The page experience update is a slow rollout that will not impact sites with huge ranking shifts. The update combined the existing core web vitals and other page experience signals to ensure that all pages are mobile-friendly. This update is more about the user experience of your site.
The spam update was said to begin on June 28; however, it started on July 26. It was rolled out over a two-week period. Google noted that this update is “even more effective at identifying and nullifying links broadly, across multiple languages.” Google also wrote a blog named ‘A reminder on qualifying links and our link spam update’ the entire post focus is on a reminder on the types of links that are against Google’s webmaster guidelines.
Final thought
While you don’t have to wait until a core update has rolled out to come up with a strategy on what to do next on your site, there are plenty of elements that you can work on, such as your core web titles as well as your website E.A.T as well Core Web Vitals.
Start by checking your rankings to see if any of the rolled-out core updates affected your site negatively or positively before making any drastic changes. Remember doing a site audit after each core update could save you from otter body shock after each update.


