URL Structuring for SEO
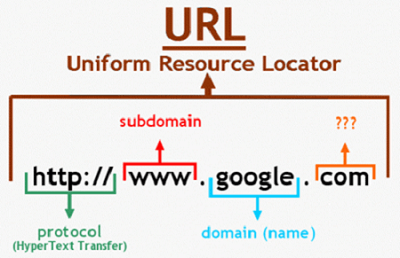
So, if we were to take a guess, you’re probably thinking “what is a URL structure?” right now. Well, a URL structure explained is essentially how you structure your page URLs. A URL, which is short for Uniform Resource Locator, is the location of your page on the web. A complete URL structure breakdown would consist of the following parts:
http:// or https:// – which indicates the protocol
www.domain.com – which is your page’s domain
/folder-name/ – is a folder on the web server (not all pages have to be in a folder or parent page)
web-page-file-name – the actual web page
Why Do You Need a Good URL Structure?
First, your URL is the first thing that search engines and web visitors see. A good URL structure prevents endless redirects, which is good for your site. And lastly, URLs are a building block for an effective site hierarchy.
Take a look at image below, would you click on such a URL? We hope not! Why? Because it is not clearl on what the page is about. It surely has many redirect loops, and it does not look secure at all.

Best URL Structure for SEO 2018
Getting your URL structure right is good for Google, user experience and for your site overall. Below are some of important pointers for a good URL structure for SEO:
- Use targeted keywords – using relevant keywords on a URL simply tells crawlers and your webpage visitors what the page is all about. So, do some keyword research and include keywords that are relevant. Tools such as https://keywordtool.io/ and https://www.semrush.com can assist with your keywords.
- Keep a simple URL structure – there are two types of URL structures, and are as follows:

One that flows from domain to category/parent page to product/actual page. e.g. domain.com/blog/home-decor-ideas-2018/
One that goes from domain to product/actual page. e.g. domain.com / home-decor-ideas-2018/
The first example is considered best for SEO. It shows that the page you’re visiting is a blog; if it were news obviously the folder name would be /news/. This is good hierarchy. Whereas, the second URL structure does not tell you what category the page you’re visiting is. This structure works well with core pages.
- Avoid unneeded characters or words
Stop Words – “and”, “or”, “but”, humans and bots can make sense of URLs without conjunctions.
Keyword repetition – for example: www.google.com/google-webmaster-tools.
Hashes # – avoid using them in some circumstances, although they can be useful. Make some of your content available via another URL.
Word delimiters – substitute underscores with hyphens. Underscores serve to join two words together.
- Keep URLs short – the shorter the better. Your URLs should be below 100 characters at most, of course depending on the page, and not longer than 2048 characters.
Protocol & Subdomains: WWW vs. Non-WWW & HTTP vs. HTTP
Protocol and subdomains make the first part of the URL. However, these are mostly taken care of by developers. So, search engines index two major versions of your site’s domain. These are the www and non-www versions. www.domain.com takes you straight into a site without having to redirect. Whereas, domain.com (without the WWW) has to redirect into the site.

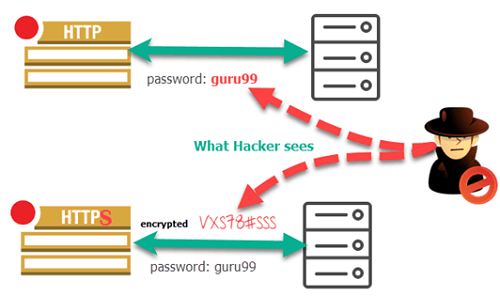
The same applies to having a secure (https), which Google prefers the most, and a non-secure (http) version.
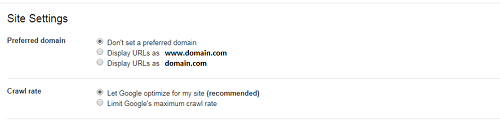
Webmasters can use either a canonical tag or 301 to point to one version to another or alternatively specify their preferred version on Google Search Console via Configuration >Settings>Preferred Domain. The setting is important because some of your backlinks could be going to just one version according to www.searchenginejournal.com.
The Effectiveness of XML Sitemaps for URLs
An XML sitemap lets search engines know what’s going on with your site. It is essentially a list of your site’s URLs that you submit to search engines. So, for Google to read/find your web pages easily and to reference when choosing canonical URLs on your site, you need to have an XML sitemap. It’s advised that you resubmit sitemaps to Google quite often, at least twice a week.
More so, the XML sitemap is not to be confused with the HTML sitemap, which is mostly designed for visitors to easily navigate around the site, and other uses.
Overview: URL Structure Best Practices for SEO
URL structuring is one of the best practices for SEO. The URL is what they first see and then decide if they would like to go onto a page or not. So, a good URL can improve the number of clicks you get and a whole lot more. More so, Google likes well-structured URLs. Try using this guide for better rankings!
Download our presentation for URL Structuring.
Like this blog? Please leave your comment below!